Table of Contents
Corporate fraud is a serious issue that affects businesses of all sizes. It involves intentional deception for financial or personal gain and can significantly damage a company’s reputation, finances, and operations. Internal investigations play a critical role in identifying and addressing fraudulent activities within an organization. These investigations help ensure compliance, protect assets, and reinforce ethical business practices. In this guide, we will explore corporate fraud, its impact, and the steps involved in conducting an internal investigation, along with best practices and challenges faced in the process.
What Is Corporate Fraud?
Corporate fraud refers to illegal activities conducted by individuals or companies to gain an unfair advantage. It can take many forms, including:
- Financial Statement Fraud – Manipulating financial reports to present misleading information to investors or regulators.
- Insider Trading – Using non-public information for personal financial gain.
- Embezzlement – Illegally taking company funds or assets for personal use.
- Bribery and Corruption – Offering or accepting bribes to influence business decisions.
- Cyber Fraud – Using technology to commit financial crimes, such as phishing scams and identity theft.
These fraudulent activities often involve misrepresentation, concealment, or breach of trust to manipulate financial records or misappropriate company resources.
Fraudulent activities not only result in financial losses but also lead to legal repercussions, regulatory penalties, and loss of stakeholder confidence. High-profile corporate fraud cases, such as Enron and WorldCom, highlight the devastating impact such misconduct can have on businesses and economies. Recognizing the signs of fraud such as sudden financial discrepancies, unauthorized transactions, or conflicts of interest can help organizations take early action to mitigate risks.
The Importance of Internal Investigations
Internal investigations play a vital role in corporate governance, helping organizations identify and address fraudulent activities before they escalate into significant issues. These investigations ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, protect a company’s financial stability, and uphold its reputation. A proactive approach to misconduct prevents costly legal liabilities and regulatory penalties. Key Benefits of Internal Investigations include:
- Ensuring Compliance and Reducing Legal Risks
By conducting thorough internal investigations, companies can ensure adherence to laws and regulations, avoiding penalties from regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Department of Justice (DOJ). - Promoting Transparency and Accountability
A well-executed internal investigation fosters an ethical workplace culture. Employees are more likely to uphold integrity when they see that misconduct is taken seriously and addressed promptly. - Enhancing Stakeholder Trust
Companies that prioritize internal investigations demonstrate a commitment to ethical business practices, strengthening trust among investors, customers, and employees. - Strengthening Internal Policies and Procedures
Investigations help identify weaknesses in governance structures and operational workflows. Addressing these vulnerabilities enables businesses to implement stronger preventive measures against future fraud and misconduct.
By integrating robust internal investigation processes, organizations not only mitigate financial and reputational risks but also create a more accountable and transparent work environment.
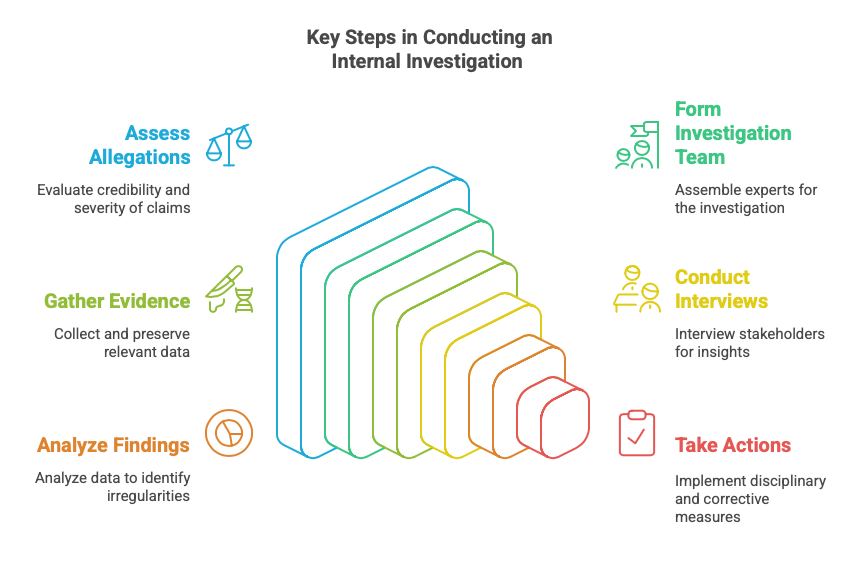
Key Steps in Conducting an Internal Investigation
- Receiving and Assessing Allegations – Organizations should establish clear reporting mechanisms, such as anonymous hotlines or designated compliance officers, to receive fraud complaints. All allegations must be evaluated for credibility, severity, and potential impact before launching a formal investigation. Organizations must ensure confidentiality to encourage employees to report misconduct without fear of retaliation.
- Forming an Investigation Team – A specialized investigation team should be assembled, comprising legal experts, compliance officers, and forensic specialists. In complex cases, involving external auditors or legal professionals may provide additional expertise and unbiased insights. The team must define its scope, objectives, and timeline before proceeding further.
- Gathering Evidence – Investigators should collect and review relevant documentation, including financial records, emails, internal reports, and transaction logs. Advanced digital forensic tools can help retrieve deleted data and uncover hidden financial discrepancies. Maintaining chain-of-custody procedures is crucial to preserving the integrity of the evidence.
- Conducting Interviews – Structured interviews with employees, vendors, or clients can provide valuable insights into fraudulent activities. Investigators should use open-ended questions and behavioral analysis techniques to detect inconsistencies in responses. Witness statements should be documented thoroughly, and legal guidelines must be followed to avoid coercion.
- Analyzing Findings – Once evidence is collected, it should be meticulously analyzed through forensic accounting, data analytics, and pattern recognition techniques. Investigators must identify irregularities, assess financial damage, and determine if there were any procedural lapses that facilitated the fraud. Collaborating with data analysts can enhance the accuracy of findings.
- Taking Disciplinary and Corrective Actions – If fraud is confirmed, disciplinary actions such as termination, suspension, or legal prosecution should be executed based on company policies and regulatory requirements. Beyond punitive measures, organizations should implement corrective actions, such as policy revisions, internal audits, and strengthened financial controls, to prevent future occurrences.
- Reporting and Documentation – The final stage involves preparing a comprehensive report detailing the investigation’s scope, methodologies, findings, and recommendations. Transparency in reporting fosters accountability and ensures regulatory compliance. Organizations should also communicate findings to relevant stakeholders, such as senior management, regulatory bodies, and legal authorities where applicable.
Best Practices and Tools for Internal Investigations
To conduct effective fraud investigations, companies should implement a combination of structured processes, employee awareness, and advanced technologies. Here are some best practices:
- Establish a Whistleblower Program – Encourage employees to report suspicious activities without fear of retaliation. Anonymity and protection policies help foster trust and increase reporting rates. Implementing a secure whistleblower hotline or digital reporting system further strengthens fraud detection.
- Leverage Forensic Technology – Utilize data analytics, AI-powered fraud detection software, and forensic accounting tools to uncover anomalies in financial transactions, emails, and operational records. Machine learning can help identify suspicious patterns and detect fraud earlier.
- Maintain Confidentiality – Protecting the integrity of the investigation prevents evidence tampering and ensures a fair process. Restricted access to sensitive data and secure documentation storage are critical for maintaining secrecy.
- Collaborate with Legal Experts – Engaging legal counsel ensures compliance with state and federal laws, reducing the risk of litigation. Lawyers can also guide companies in handling evidence collection, employee interviews, and reporting obligations.
- Regular Training and Awareness Programs – Educating employees about fraud risks, ethical business practices, and detection methods helps prevent misconduct. Conducting periodic fraud risk assessments and compliance workshops builds a vigilant workforce.
Pro Tip: Implement a fraud risk assessment framework to identify vulnerabilities before an incident occurs. Regular audits, real-time transaction monitoring, and anonymous reporting mechanisms significantly reduce fraud risks, ensuring a more resilient corporate environment.
Challenges in Corporate Fraud Investigations
Investigating corporate fraud is a complex and sensitive process that requires careful planning and execution. Companies must navigate various legal, ethical, and operational challenges while ensuring that investigations are thorough and unbiased.
1. Lack of Cooperation
Employees or stakeholders involved in fraudulent activities may refuse to provide information or may even obstruct the investigation process, leading to delays and difficulties in gathering critical evidence. This lack of cooperation can come from individuals who fear reprisal, legal consequences, or damage to their own reputation. Furthermore, employees who are unaware of the consequences of fraud might be reluctant to engage due to workplace culture or organizational politics.
How to Overcome It:
- Encouraging Whistleblowing: Companies can implement secure, anonymous reporting systems, such as hotlines or web portals, to allow employees to report fraudulent activities without fear of retaliation.
- Building Trust: Establishing a culture of integrity and transparency through leadership can foster an environment where employees feel safe to share information.
- Incentives for Reporting: Offer financial rewards, legal protection, or career incentives for employees who provide critical information that leads to the identification of fraud. This can motivate individuals to come forward, even if they are unsure about the consequences of their actions.
2. Data Privacy Concerns
Navigating data privacy laws, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), while collecting digital evidence can be a significant challenge. These laws impose stringent rules on how personal data is collected, processed, and stored. When investigating fraud, especially if it involves employee or customer data, companies may face legal consequences if they inadvertently breach these privacy laws. Moreover, unauthorized access to sensitive data could result in public backlash, regulatory penalties, and reputational harm.
How to Overcome It:
- Strict Compliance: Ensure that all data collection processes align with relevant privacy laws and regulations by working closely with legal and compliance teams.
- Data Minimization: Limit the scope of data collection to only what is necessary for the investigation. Avoid accessing personal information that is not directly related to the fraudulent activity under investigation.
- Obtain Approvals: Before accessing personal data or implementing surveillance, always obtain explicit consent from relevant parties or necessary legal authorization to avoid violating privacy regulations.
3. Reputational Risks
Mishandling an investigation or failing to address fraud adequately can significantly damage a company's reputation. The public perception of the company’s ability to detect, prevent, and respond to fraud plays a crucial role in maintaining trust with investors, customers, and employees. If fraud is uncovered in a poorly managed investigation, it can lead to loss of customer loyalty, reduced stock value, and even legal consequences. Furthermore, if the company is perceived as slow to act or dismissive of its fraud detection efforts, it may tarnish its brand image permanently.
How to Overcome It:
- Transparent Communication: Maintain open and honest communication with stakeholders, updating them on the investigation’s progress, findings, and any corrective actions being taken. Transparency helps manage expectations and reduces the possibility of rumors or misinformation spreading.
- Proactive Damage Control: In case of any lapses in handling the investigation, take immediate and decisive actions such as issuing public apologies, conducting internal reviews, and implementing stronger fraud prevention measures. Demonstrating accountability can help mitigate damage to the company's reputation.
- Ethical Investigative Practices: Ensure that the investigation is carried out in a fair and transparent manner, respecting the rights of all involved parties. Upholding ethical standards throughout the process will reflect positively on the company’s commitment to integrity.
4. Legal and Compliance Complexities
Corporate fraud investigations must adhere to a range of legal and regulatory requirements, which can vary depending on the jurisdiction and industry. Investigators need to ensure that the evidence they collect is admissible in court and that the investigation process itself complies with both federal and state laws. Failure to do so could result in evidence being thrown out, lawsuits, or regulatory sanctions. Moreover, the legal landscape is constantly evolving, making it difficult to keep up with the latest regulations that may impact the investigation.
How to Overcome It:
- Work with Legal Experts: Engage legal counsel and compliance officers early in the investigation to ensure that all actions taken align with legal standards and industry-specific regulations.
- Stay Updated on Regulations: Regularly monitor updates to relevant laws and regulations to ensure ongoing compliance. This includes changes to fraud detection laws, privacy regulations, and corporate governance guidelines.
- Internal Audits: Perform internal audits on a routine basis to identify any vulnerabilities in fraud prevention systems, and ensure that your compliance protocols are robust and up-to-date. Regular audits help catch potential legal issues early on and reduce the likelihood of breaches.
5. Resource Limitations
Small and mid-sized companies, in particular, may lack the necessary resources, both in terms of personnel and financial investment, to conduct thorough fraud investigations. Limited budgets may restrict access to specialized tools, forensic experts, or third-party investigations, hindering the company’s ability to detect and resolve fraud effectively. Smaller teams may also struggle to devote enough time to investigate fraud, leading to potential oversight or incomplete investigations.
How to Overcome It:
- Invest in Fraud Detection Technology: Companies can leverage automation tools and fraud detection software that can help identify suspicious activity quickly and accurately. This reduces the reliance on manual processes and ensures a more effective and timely response.
- Outsource Forensic Audits: Smaller organizations can partner with external forensic accounting firms or investigative agencies that specialize in fraud detection. These experts bring in-depth knowledge and resources that can be costly to develop in-house.
- Train Internal Teams: Invest in training internal employees to recognize signs of fraud and equip them with the skills to conduct preliminary investigations. By building internal expertise, companies can reduce their reliance on external resources and handle more cases in-house.
Conclusion
Corporate fraud poses a significant threat to businesses, making internal investigations a crucial component of risk management. Fraudulent activities can result in financial losses, legal consequences, and reputational damage, ultimately affecting long-term sustainability. Organizations must proactively implement fraud detection mechanisms, enforce ethical standards, and respond swiftly to any suspicious activities to safeguard their operations.
NSKT Global provides expert fraud detection, forensic accounting, and risk assessment services to help businesses combat fraud effectively. Their specialized team assists organizations in compliance monitoring, financial auditing, and investigative techniques, equipping them with the necessary tools to detect and mitigate fraud. With advanced forensic tools and data-driven insights, NSKT Global helps businesses identify vulnerabilities, strengthen internal controls, and ensure regulatory compliance.
By leveraging NSKT Global’s expertise, organizations can build a strong fraud prevention strategy, protect assets, and foster a culture of transparency and accountability. A proactive approach ensures stability and minimizes financial and reputational risks in an evolving business environment. Fraudulent activities can lead to financial losses, legal consequences, and reputational damage, impacting long-term growth and stability. Organizations must proactively establish fraud detection mechanisms, enforce ethical standards, and respond swiftly to any suspicious activities to safeguard their operations.
FAQs About Corporate Fraud and Internal Investigation
- What are the most common types of corporate fraud that organizations should watch out for?
Asset misappropriation, financial statement fraud, bribery, corruption, and cyber fraud. - How can internal investigations help mitigate the financial and reputational risks of fraud?
They identify fraud early, prevent financial losses, ensure compliance, and maintain stakeholder trust. - What key steps should be followed when launching an internal investigation?
Define scope, gather evidence, interview witnesses, maintain confidentiality, analyze findings, and take corrective action. - Which tools and technologies can enhance the effectiveness of fraud investigations?
AI-powered fraud detection, forensic accounting software, data analytics, digital forensics, and secure whistleblower platforms. - What are the main challenges in conducting an independent internal investigation, and how can they be overcome?Challenges include non-cooperation, legal complexities, data privacy issues, and resource constraints; they can be mitigated with legal guidance, forensic tools, and strong compliance policies.



